What You Should Know:
- Since the Arch Collaborative’s early days, analysis of clinician feedback has identified three pillars key to EHR satisfaction: (1) strong user mastery, (2) an organization-wide sense of shared ownership, and (3) EHR technology that meets users’ unique needs (personalization).
- This last pillar is the focus of this report. While it is important for physicians to have the flexibility to care for patients and document in a way that fits their workflow, too much freedom to change the EHR can hinder efficiency and patient safety. This report identifies the benefits of personalization as well as best practices for leveraging it
Insights into the Personalization of EHR in 2023
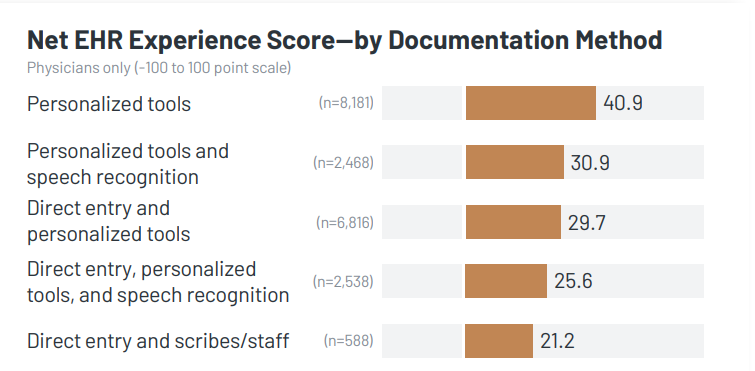
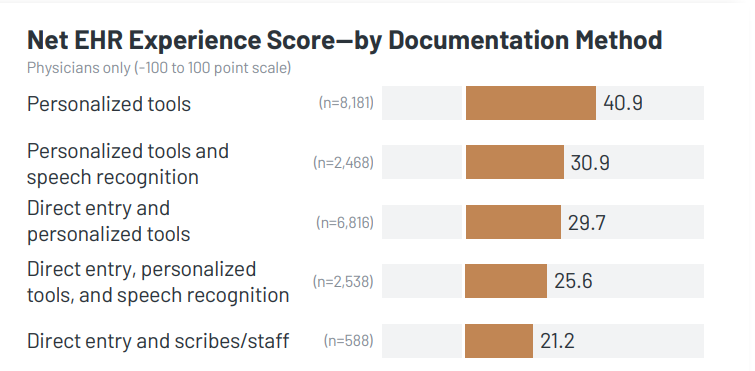
- Physicians Who Use Personalized Tools for Documentation Report Highest EHR Satisfaction: Although direct entry is the most common documentation approach, utilizing personalized tools is strongly associated with higher Electronic Health Record (EHR) satisfaction, as measured by the Arch Collaborative’s Net EHR Experience score (NEES). While alternative methods like dictation/transcription and speech recognition may alleviate burnout (refer to the chart on the following page), they distance users from the EHR, diminishing the potential for enhanced satisfaction. In contrast, individuals who customize the EHR display a commitment to mastering the technology rather than disengaging from it. Physicians who employ personalized tools for documentation, whether independently or in combination with other methods, exhibit an average NEES score 15.5 points higher than those who do not embrace personalized tools.
- Use of Multiple Documentation Methods Correlated with Higher Rates of Burnout: Except for physicians who utilize both dictation/transcription and direct entry, those who rely solely on one documentation method, regardless of its nature, generally report lower levels of burnout. Furthermore, physicians employing multiple documentation approaches are more prone to attribute their burnout to after-hours charting compared to those employing a single documentation method. As previously mentioned, physicians using dictation/transcription or speech recognition tend to experience reduced burnout but not an increase in EHR satisfaction, likely due to these methods disconnecting users from the EHR rather than promoting mastery of it.
- Organizations and Vendors Can Support High EHR Satisfaction through Strong Documentation Training: Organizations seeking to enhance EHR satisfaction by implementing personalized tools or any documentation approach should prioritize their documentation training programs. Irrespective of the chosen documentation method, there exists a significant gap of at least 30 points in NEES between physicians who deem their documentation training as satisfactory and those who do not. Several factors contribute to this discrepancy, with a primary one being that a substantial portion of a physician’s EHR interaction time is devoted to documentation. Enhanced training in efficient and effective documentation methods is key to physicians’ overall success with the EHR.