Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based innovator pharmaceuticals have seen an 800% growth in total licensing agreement deal values from 2019 to 2024YTD, according to GlobalData’s Pharma Intelligence Center Deals Database.
mRNA-based vaccines, which work by instructing cells to produce specific proteins that can prevent or treat various diseases, show great promise in precision medicine for treating infectious diseases, genetic disorders, and cancers. The Covid-19 pandemic highlighted the significant advantages of the technology in vaccine development, including its rapid development, precise immune targeting, and streamlined manufacturing process—factors that contributed to the success of mRNA-based Covid-19 vaccines.
Since the FDA approved Pfizer‘s Comirnaty in August 2021, the first mRNA vaccine to enter the global market, there has been a surge in designations for mRNA vaccines, reaching a record ten designations in 2023 alone. This growth has continued into 2024, with the rising value of licensing agreements reflecting growing confidence in this technology beyond application in vaccines. Global sales for innovator mRNA-based pharmaceuticals reached $22bn in 2023 and is projected to increase to $26.2bn by 2030, according to GlobalData’s Drugs Database.
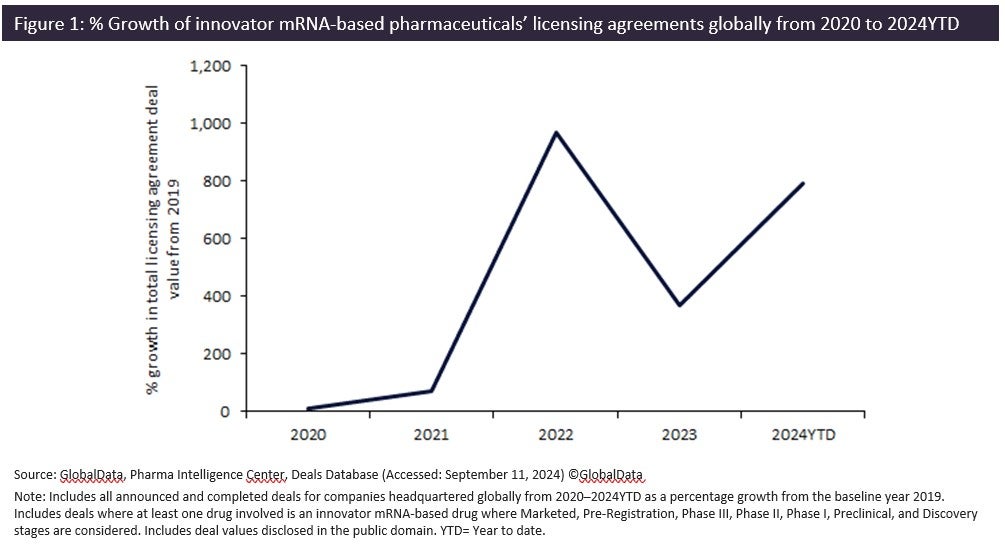
mRNA-based pharmaceuticals’ licensing agreement deal values doubled since 2023 to reach $3.8bn, with large pharma companies like GSK and Bristol Myers Squibb investing in the development of mRNA therapeutics and recognising their potential to address unmet medical needs across a range of diseases.
In July 2024, GSK and Curevac restructured their 2020 collaboration into a new licensing agreement worth up to $1.57bn. This agreement focuses on the development, manufacturing, and commercialisation of mRNA vaccine candidates for influenza and Covid-19, covering stages from preclinical to Phase II trials.
Similarly, in April 2024, Bristol Myers Squibb entered a multi-year strategic collaboration with Repertoire Immune Medicines, a biotech company specialising in programmable T cell-targeted immune therapies. Valued at up to $1.87bn, this collaboration aims to develop mRNA-based tolerising vaccines for up to three autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis, as well as other vaccine candidates.
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Your download email will arrive shortly
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalData
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), which provides grants and financial support for biomedical research including the development of new therapies and vaccines, recently reinforced the importance of this technology by committing $176m to Moderna for the development of mRNA-based vaccines targeting multiple strains of pandemic influenza.
This initiative emphasises a continued focus on enhancing pandemic preparedness and response, further validating the potential and adaptability of mRNA platforms. The rise in mRNA pharmaceuticals’ licensing agreement values suggests that this field will remain a major area for innovation and investment. As mRNA technology and delivery systems advance, the potential for drugmakers to expand their mRNA portfolios is substantial, promising significant breakthroughs in the treatment of various diseases.
